Payloads
The wiki is being retired!
Documentation is now handled by the same processes we use for code: Add something to the Documentation/ directory in the coreboot repo, and it will be rendered to https://doc.coreboot.org/. Contributions welcome!
coreboot in itself is "only" minimal code for initializing a mainboard with peripherals. After the initialization, it jumps to a payload.
Payloads
Bootloaders
GRUB2
GRUB2 is the standard bootloader for Linux and other Unix-like operating systems.
You can use GRUB2 as a coreboot payload, too, in order to boot and operating system from a hard drive, for instance.
FILO
FILO is a simple bootloader with filesystem support.
It will be deprecated in favor of GRUB2 soon.
Operating systems
Linux
Coreboot can use a Linux kernel as payload directly. That is, the kernel is included in the ROM chip where coreboot resides.
Alternatively, you can also boot a Linux kernel from your hard drive using either the FILO or GRUB2 payloads, of course.
FreeBSD
FreeBSD can be booted via coreboot with the help of ADLO.
OpenBSD
OpenBSD can also be booted via coreboot with the help of ADLO.
This use-case is not well-tested yet, though.
Windows
Windows can be booted with the help of ADLO.
This use-case is not well-tested yet, though.
Other
Open Firmware
Mitch Bradley's Open Firmware, an IEEE1275-1994 Open Firmware implementation, can also be used as coreboot payload.
OpenBIOS
OpenBIOS — IEEE1275-1994 Open Firmware.
Etherboot
Etherboot — Includes FILO, and its FILO supports SATA and USB booting.
Memtest86 / Memtest86+
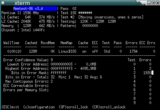
Memtest86 is a program which checks your RAM modules.
It can be run from within GRUB, but also as a coreboot payload (i.e. included in your ROM chip).
ADLO
ADLO — Glue layer to 16-bit Bochs BIOS. Allows booting Windows and OpenBSD.
Libpayload
Libpayload is a helper-library for payload-writers.
Coreinfo
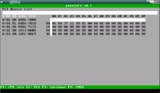
coreinfo is a coreboot payload which can display various system information.
Games
GRUB invaders
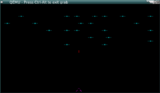
GRUB invaders multi-boot compliant space invaders game.
It can either be started from within GRUB (as a "kernel"), or it can be used as a coreboot payload.
TINT
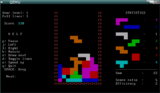
tint is a falling blocks game.
Possible future payloads
The following payloads might or might not work (with more or less changes required) with coreboot — their usage hasn't been tested or documented so far.
- CodeGen's SmartFirmware — IEEE1275-1994 Open Firmware
- GNUFI (UEFI)
- Plan 9 — A distributed operating system.
- RedBoot / eCos — Real-time OS for embedded systems; initial port to ELF completed but no longer available.
- GPXE — Needs some code changes
- OpenSolaris — See this blog entry
- NetBSD — Work in progress
- HelenOS
- ReactOS
History
The payload was originally intended to be a Linux kernel stored in flash. Flash ROM growth rate was anticipated optimistically however, today there are not many mainboards that actually have enough flash ROM room for a kernel. 512KB can be seen here-and-there and a few boards come with 1MB. Recent kernels really want that MB, and then you'll only have room for 300-400 KB of initial ramdisk, which could be too small too, depending on the application. During testing, a payload may also be downloaded via X-Modem from the serial debug console, saving flashing time.
So, other payloads are used; the two major ones are FILO and Etherboot. FILO loads a kernel from a filesystem on an IDE device and Etherboot loads a kernel from the network or from a filesystem on an IDE device.
If you're using FILO there is no Linux kernel until FILO loads it, and the kernel loaded by FILO (or Etherboot) can absolutely be the one you want to run in your system. Just set it up with the correct root and init commandline so that it can start init.